How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after, opening doors to stunning aerial photography, videography, and even professional applications. This guide provides a structured approach to mastering drone piloting, covering everything from pre-flight checks and safety protocols to advanced camera techniques and legal considerations. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your existing skills, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We will explore the intricacies of drone controls, navigating different flight modes, and mastering image capture. We’ll also delve into crucial aspects like battery management, maintenance, and legal compliance, ensuring your drone operation is not only successful but also adheres to all relevant regulations. By the end, you’ll possess a robust understanding of how to operate a drone, transforming you from a novice into a confident and capable pilot.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone’s components, assessing weather conditions, and understanding emergency procedures. Responsible operation near people and property is also paramount.
Drone Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection ensures the drone is in optimal condition. The following table Artikels key components and their acceptable/unacceptable conditions.
| Component | Inspection Item | Acceptable Condition | Unacceptable Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Damage, tightness | No cracks or chips; securely fastened | Cracks, chips, or loose propellers |
| Battery | Charge level, physical condition | Sufficient charge; no visible damage or swelling | Low charge; damage, swelling, or leaking |
| Gimbal | Movement, stability | Smooth, stable movement in all directions | Jerky movement, loose components, or noise |
| Camera | Lens clarity, functionality | Clean lens; proper image preview | Dirty or scratched lens; malfunctioning camera |
Weather Conditions
Adverse weather can significantly impact drone flight safety and performance. Always check the forecast before flying. Conditions that should prevent flight include:
- High winds (exceeding the drone’s wind resistance capabilities)
- Heavy rain or snow
- Dense fog or low visibility
- Lightning or thunderstorms
Emergency Procedures
In case of a drone malfunction or loss of control, immediate action is necessary. This may involve:
- Initiating the Return-to-Home (RTH) function (if available)
- Attempting to regain control using manual maneuvers
- If control cannot be regained, safely land the drone in a clear area, prioritizing safety over the drone’s condition.
- Contacting relevant authorities if the drone poses a safety risk.
Responsible Operation Near People and Property

Operating a drone responsibly near people and property is essential. Maintain safe distances, and always adhere to local airspace regulations. Generally, you should maintain a significant distance from people and structures (check local regulations for specifics).
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to check out is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering the art of drone operation requires practice and patience, but the rewards of capturing stunning aerial footage are well worth the effort.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Mastering drone controls is crucial for safe and effective flight. This section covers basic controls, flight modes, and fundamental maneuvers.
Drone Controls

A typical drone remote has two control sticks and several buttons. Each control affects the drone’s movement in a specific way:
- Left Stick: Controls the drone’s yaw (rotation) and throttle (vertical movement).
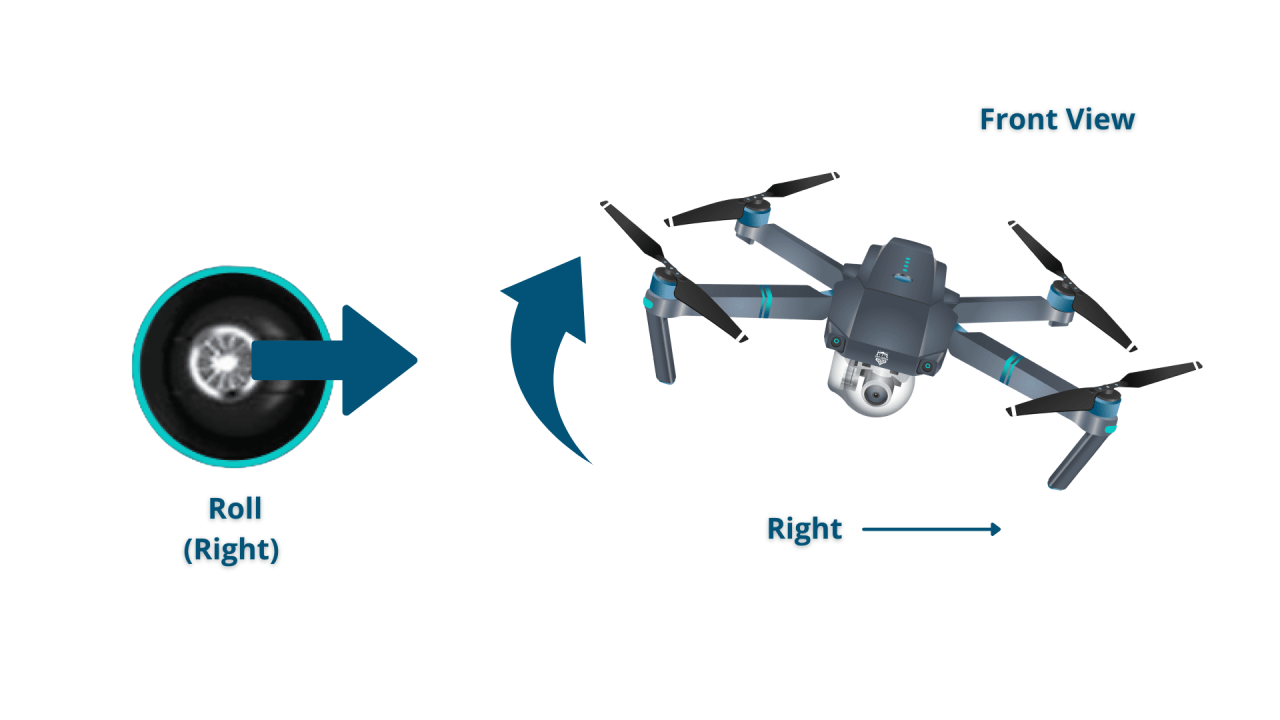
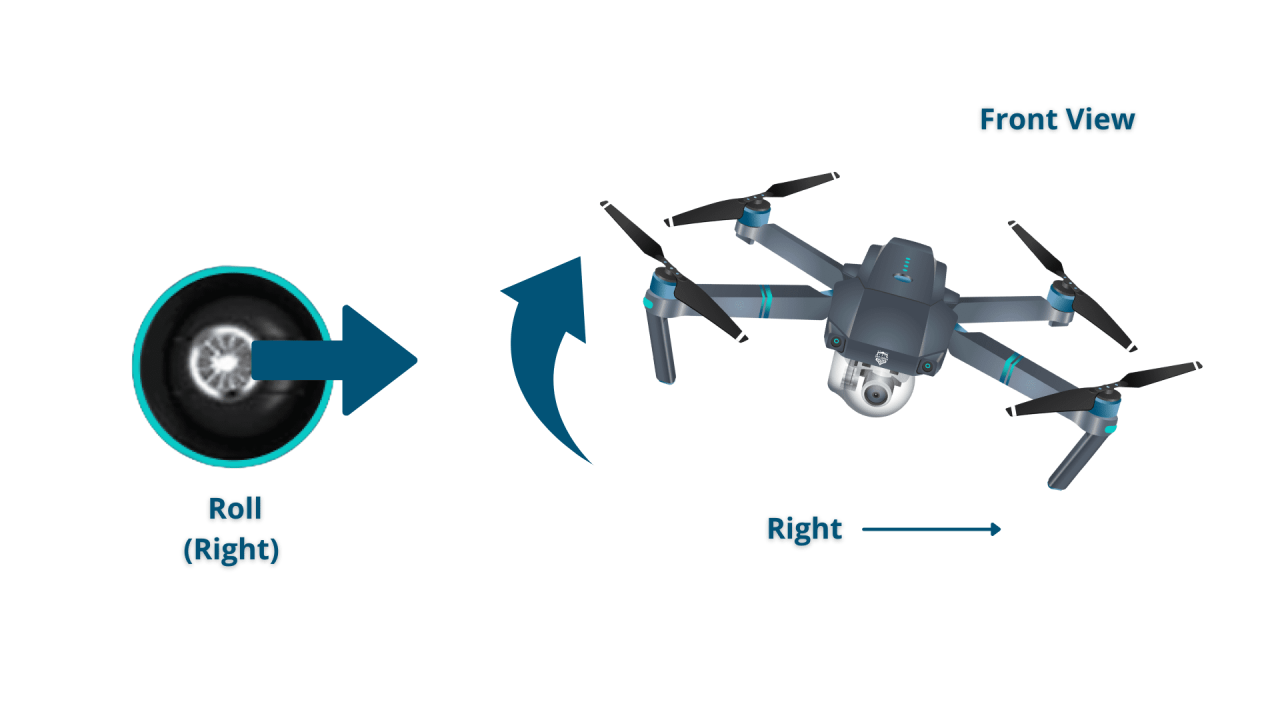
- Right Stick: Controls the drone’s pitch (forward/backward movement) and roll (left/right movement).
- Return-to-Home (RTH) Button: Initiates an automated return to the home point.
- Emergency Stop Button: Immediately stops the motors.
- Camera Control Buttons: Adjust camera settings such as zoom, photo/video recording.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of stability and control. GPS mode utilizes satellite signals for positioning, while Attitude mode relies on onboard sensors for orientation. Understanding the differences is crucial for adapting to various flight conditions.
- GPS Mode: Offers greater stability and precision, particularly useful for beginners.
- Attitude Mode: Provides more responsive control but requires more skill to prevent drifting.
Takeoff, Hover, and Landing
These are fundamental steps in any drone flight. The exact procedure might vary slightly depending on the drone model, but the principles remain the same.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Calibrate the compass (if necessary).
- Slowly increase throttle to lift off gently.
- Maintain a stable hover using the control sticks.
- Slowly decrease throttle to land gently.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Basic Maneuvers
Once comfortable with takeoff, hover, and landing, you can practice basic maneuvers. These include turning, ascending, and descending.
- Turning: Use the left stick to rotate the drone.
- Ascending: Gently increase the throttle (left stick).
- Descending: Gently decrease the throttle (left stick).
Camera Operation and Image Capture
Understanding camera settings and techniques is essential for capturing high-quality images and videos. This section covers camera settings, lighting adjustments, and shot composition.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to safely and effectively handle a drone is crucial, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone. This website provides comprehensive guidance on various aspects of drone piloting, ultimately helping you to confidently and responsibly operate your drone.
Proper training ensures safe and enjoyable drone flights.
Camera Settings
Camera settings significantly impact image quality. ISO, shutter speed, and aperture are key parameters to adjust.
| Setting | Effect on Brightness | Effect on Sharpness | Effect on Depth of Field |
|---|---|---|---|
| High ISO | Brighter | Potentially grainier | No effect |
| Low ISO | Darker | Sharper | No effect |
| Fast Shutter Speed | Darker | Sharper (freezes motion) | No effect |
| Slow Shutter Speed | Brighter | Blurrier (motion blur) | No effect |
| Wide Aperture (low f-stop) | Brighter | Potentially slightly softer | Shallow depth of field (blurred background) |
| Narrow Aperture (high f-stop) | Darker | Sharper | Deep depth of field (everything in focus) |
Lighting Conditions
Adjust camera settings to optimize image quality in various lighting conditions. For example, in low light, increase the ISO to brighten the image but be aware of potential grain. In bright sunlight, use a faster shutter speed to prevent overexposure.
Stable Video Footage
Smooth video footage is achieved through a combination of factors: using a gimbal, flying smoothly, and potentially using post-processing stabilization software.
Shot Composition
Effective shot composition enhances visual appeal. Consider the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional techniques to create visually engaging content.
Battery Management and Flight Time
Proper battery management is crucial for maximizing flight time and ensuring safe operation. This includes charging, storing, and monitoring battery health.
Charging and Storing Batteries, How to operate a drone
Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow charging instructions carefully. Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
Factors Affecting Flight Time
Several factors influence flight time, including weather conditions, payload weight, and flight style. High winds, heavy payloads, and aggressive flight maneuvers will reduce flight time.
Battery Health Indicators and Maintenance
| Indicator | Description | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | Lower voltage indicates lower charge | Charge the battery |
| Cycle Count | Number of charge-discharge cycles | Replace battery after a certain number of cycles (consult manufacturer’s specifications) |
| Physical Condition | Swelling, damage, or leaks | Replace damaged batteries |
Managing Multiple Batteries
For extended flight sessions, carrying multiple batteries is essential. Always keep spare batteries charged and ready to replace depleted ones. Follow manufacturer’s guidelines for safe battery handling and replacement.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting skills are essential for keeping your drone in top condition and resolving common issues.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule should include cleaning the drone’s body, propellers, and camera lens. Inspect all components for any signs of wear and tear.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Common malfunctions include low battery, GPS signal loss, and motor problems. Low battery is usually caused by overuse or old batteries, GPS signal loss can result from interference or poor satellite reception, and motor problems can stem from physical damage or wear and tear.
Troubleshooting Steps
For low battery, charge the battery. For GPS signal loss, try moving to an open area with a clear view of the sky. For motor problems, inspect the motors for damage.
Troubleshooting Flowchart (Drone Won’t Take Off)
A flowchart visually guides troubleshooting steps. This example illustrates a simplified process:
- Check battery charge level. If low, charge the battery and retry.
- Check propeller condition. If damaged, replace and retry.
- Check GPS signal strength. If weak, move to an open area with a clear view of the sky and retry.
- Check for motor issues. If detected, contact support.
- If none of the above resolves the issue, contact drone manufacturer support.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone legally and ethically requires understanding and adhering to relevant laws and regulations. This includes obtaining necessary permits, respecting airspace restrictions, and prioritizing safety and privacy.
Relevant Laws and Regulations
Drone laws and regulations vary by location. It’s crucial to research and understand the specific rules in your area. These regulations often dictate where you can fly, what you can film, and any necessary registrations or permits.
Obtaining Permits and Licenses
Depending on the type of drone operation, obtaining permits or licenses might be necessary. This process typically involves applying through the relevant aviation authority and meeting specific requirements.
Restrictions on Drone Flight
Several areas have restrictions on drone flight. These include airports, sensitive areas (military bases, power plants), and private property (without permission from the owner). Always check for no-fly zones before operating your drone.
Best Practices for Legal and Ethical Operation
Best practices include respecting privacy, avoiding flying over crowds, and obtaining necessary permissions before filming people or private property. Always operate your drone responsibly and within the bounds of the law.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding journey that blends technical skill with responsible practice. From the meticulous pre-flight checklist to the creative possibilities of aerial photography, each step contributes to a safe and enjoyable experience. By understanding drone controls, camera settings, and legal frameworks, you can unlock the full potential of this technology, capturing breathtaking visuals and expanding your horizons.
Remember, safe and responsible piloting is paramount; always prioritize safety and adhere to all regulations.
FAQ Explained: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and automated features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with good reviews and ease-of-use reputation.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country/region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific rules and procedures.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
Immediately attempt to regain control using the emergency procedures Artikeld in your drone’s manual. If unsuccessful, contact local authorities.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrating your drone’s compass before each flight is recommended, especially if you’re flying in areas with strong magnetic interference.